A learning disorder when identified in young children is commonly referred to as dyslexia. It interferes with one’s ability in speaking, reading, and write. Over 10% of Americans have been dragonized with the symptoms of dyslexia. These symptoms may include reading slowly, word jumbles, and spelling difficulties.
Dyslexia can even occur in adults. Because they had dyslexia all their lives but didn’t get a quick diagnosis. Now the question is, can dyslexia affect speech in children? To know more, continue reading about the lookouts for dyslexia.
So, let’s begin the discussion with –
Why Does Dyslexia Occur?
From difficulties in reading, spelling, and speaking – all are common symptoms of dyslexia. The developmental dyslexia is an extremely heritable condition, so you can notice that families frequently have members with this learning disability. A child’s likelihood of having dyslexia increases if their parents, siblings, and other close relatives have it.
The genetic variations account for anomalies in the areas of the brain intricate in language processing. Also, recent imaging studies of dyslexic children and adults reveal that reading does not activate all of the language-processing areas of the brain. When a person has dyslexia, their brain has trouble making the connections between letters, sounds, and words as well as between words and their meanings. After taking the best dyslexia training program online, you can get a complete understanding of the topic.
In some circumstances, a person with a very mild type of dyslexia may have fewer spelling errors as it is a spectrum disorder. Others might have a severe type that impairs daily conversation as well as reading and spelling.
How Can Dyslexia Affect Speech In Children?
The following are some major ways dyslexia can affect speech among children –
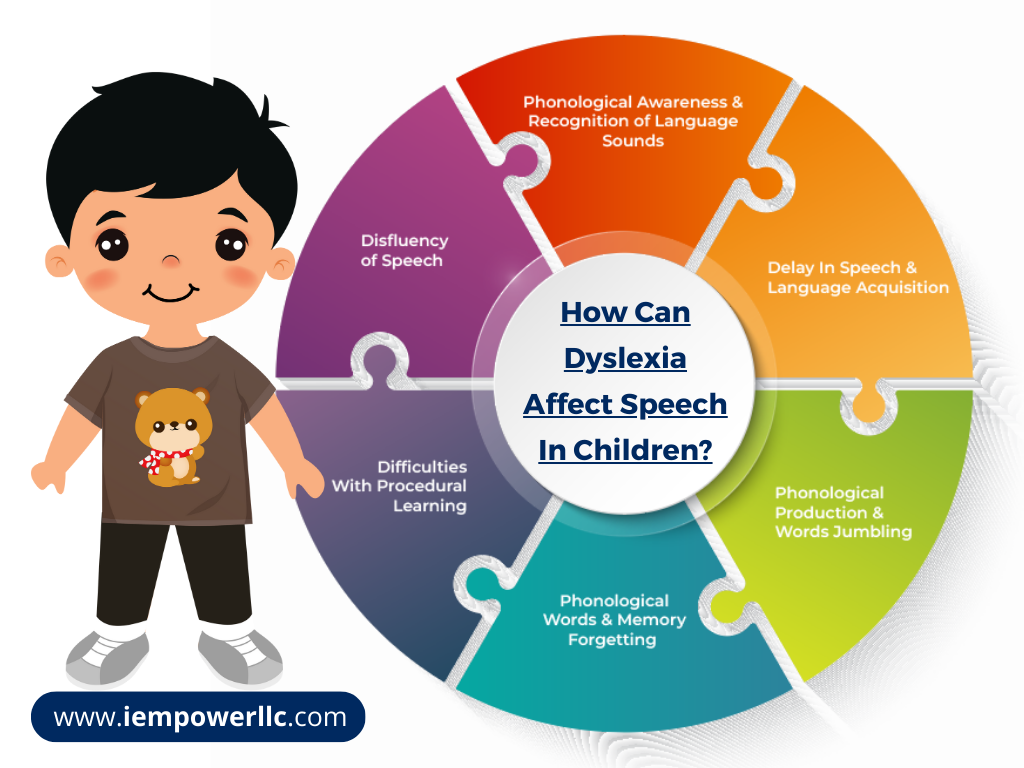
Effect 1: Phonological Awareness & Recognition of Language Sounds
It denotes a person’s ability to hear, comprehend, and differentiate among various sounds of a language. This symptom will enable individuals to manipulate and remember sounds at the syllable, phoneme, word, and sentence levels. Some dyslexic person has poor phonological awareness as well. So, they frequently struggle to remember and find the words they need to express themselves. By taking dyslexia training for teachers, hopefully, you will get to know the details of dyslexia in speech.
Effect 2: Phonological Production & Words Jumbling
People having dyslexia frequently mix up words with similar sounds, such as “cat” with “cot” because they are similar phonetically. Those having dyslexia also make the same mistakes while writing phonetic words. Therefore, it’s one of the most typical symptoms of dyslexia, to have trouble finding the appropriate word at the correct time.
Effect 3: Phonological Words & Memory Forgetting
People with dyslexia frequently find themselves looking for “the right word”. Because they frequently forget everyday and simple terms like “automobile”, “remote” and “names”. In case you are struggling to remember words that are similar, you may have dyslexia, and it could also be challenging for you to recall the precise sound combination needed to create that word.
Effect 4: Difficulties With Procedural Learning
Dyslexia further has an impact on a person’s ability in procedural learning. It affects how complicated speech-sound categories are learned by procedural learning. The difficulty people with dyslexia have understanding speech is a result of the disorder rather than its cause.
Effect 5: Disfluency of Speech
Around 5% and 30% of people are examined with dyslexia in early childhood and adult respectively. Disfluency of speech affects less than 1% of the world’s population, although it affects a significantly higher proportion of those who have dyslexia. The likelihood of disfluency is higher in those with severe dyslexia than in people with lesser types of this learning problem.
Effect 6: Delay In Speech & Language Acquisition
Your child may be dyslexic if your family has one or more dyslexic relatives and they exhibit speech delay symptoms. So, taking dyslexia training for parents will enable you to manage your child with extra care. Sometimes kids with dyslexia may take longer to learn new words and confuse terms with similar-sounding phrases when speaking. Additionally, they could struggle to pronounce and memorize names for objects, numbers, and symbols.
Best Treatment for Dyslexia
Dyslexics can benefit from speech therapy or working with a certified speech-language pathologist. A leading dyslexia training program can evaluate reading and writing abilities to support early language development through an early intervention. If this learning deficit is not treated, it may result in serious communication problems that have an impact on a person’s quality of life, ability to pursue higher education, and choice of job.
To learn more about can dyslexia affect speech in children and what treatments are available for kids and adults with dyslexia, you can simply visit us at www.iempowerllc.com to join us today!
